Chagas
Chagas is a deadly parasitic disease that kills around 12,000 each year.
Chagas is not as well known as diseases such as malaria or cholera yet it affects between six and seven million people.
It is a parasitic disease found almost exclusively in the Americas, however, with increases in global travel, cases have begun to be reported in the US and Europe.
Millions of people with the disease, including those infected decades ago, go undetected and untreated.
Without treatment, Chagas can eventually lead to fatal damage of the heart and nervous and digestive systems.
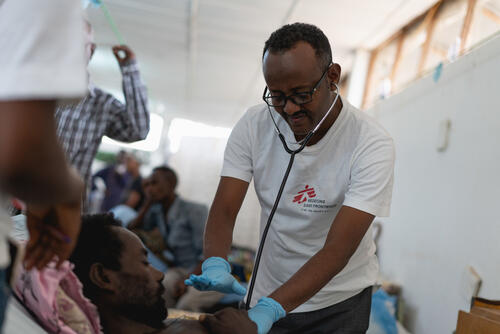
MSF teams have treated patients with Chagas disease since 1999 and worked in Bolivia, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Brazil and Nicaragua. However, existing drugs and diagnostic tests are inadequate, expensive and in short supply.
Without significant funding, MSF Chagas programmes in Latin America have an uncertain future.
Chagas disease: Key facts
6-7 MILLION
PEOPLE WITH CHAGAS WORLDWIDE
12,000
PEOPLE KILLED BY CHAGAS ANNUALLY
30%
OF PATIENTS SUFFER CARDIAC DISORDERS
What causes Chagas?
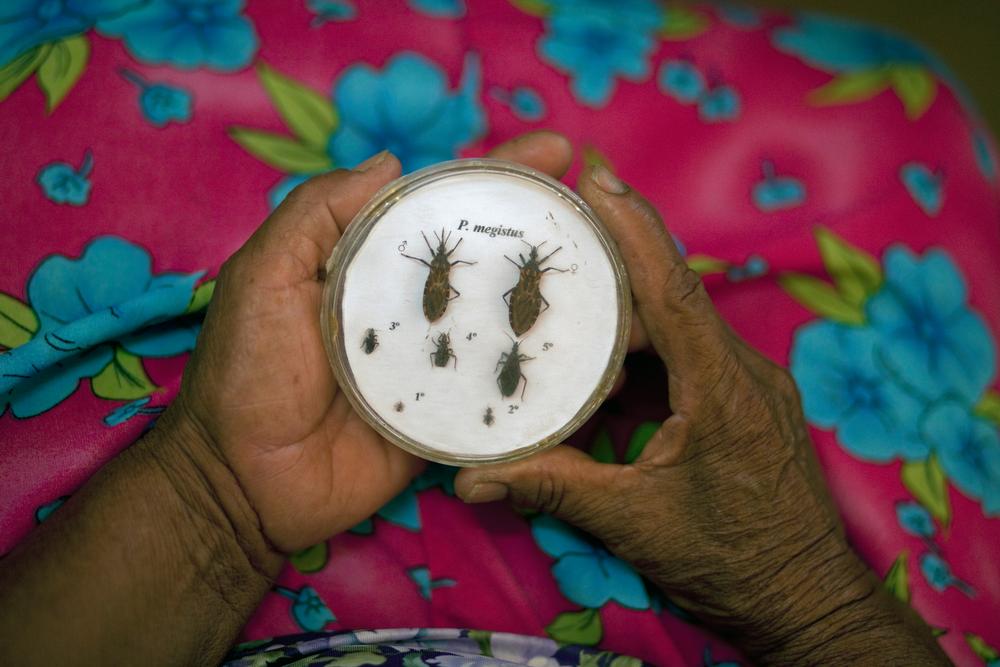
Chagas, or Trypanosoma cruzi, is a parasitic disease transmitted by an insect that lives in the walls and roofs of mud and straw housing, common in rural areas and urban slums in Latin America.
The bugs that carry the disease, known as ‘triatomines’, emerge at night to feed. Chagas has also been known to be transmitted through blood transfusions, organ transplants, breastfeeding and congenitally, through a pregnant mother to her baby.
Contracting the disease through eating or drinking infected food or water is highly unusual but it has been recorded.
Symptoms of Chagas
Chagas disease has two stages: an acute stage, shortly after infection, and a chronic stage, developing over many years. Detecting Chagas in both stages is particularly difficult.
In the acute stage - the first few weeks after infection - the infected person will show only mild symptoms, which are common in many other diseases. These can range from body aches and fatigue to fever and vomiting.
After the acute phase, Chagas goes into remission and no other symptoms may appear for many years.
About 20-30 percent of those infected will go on to develop the chronic form of the disease where the life-threatening heart and/or digestive disorders will develop, causing irreversible damage to the heart, oesophagus and colon. Symptoms at this stage might include constipation, digestive problems, pain in the abdomen and swallowing difficulties.
Diagnosing Chagas
Diagnosing Chagas disease is complicated. Doctors need to perform two or three blood tests to determine whether the patient is infected with the parasite and often these tests are inadequate, expensive and in short supply.
MSF has called for the development of new diagnostic tests.
Treating Chagas
Treatment must occur in the acute stage of the infection and because people who have been treated can easily be re-infected, treatment is more effective in areas with active vector control (the vector, in this case, being the insect that transmits the disease). To date, drugs have only been effective in the acute and asymptomatic stage of the disease.
There are currently only two medicines available to treat the disease: benznidazole and nifurtimox, which were both developed over 40 years ago.
There are few drugs that can effectively treat the disease and the current line of treatment can be toxic, taking one to two months to complete. Just like diagnostic tests for Chagas, treatments for the disease are also inadequate and expensive.
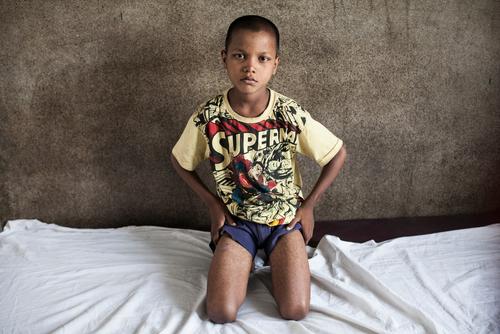
In Bolivia and Guatemala, MSF’s most effective Chagas programmes have focused on preventative measures, education and screening in children.
Spotlight: Chagas explainer
Chagas: News and stories