Diphtheria
What is diphtheria?
Diphtheria is a deadly infectious disease but is entirely preventable by vaccination.
Throughout history, diphtheria has caused devastating epidemics across the globe. Children are typically the most at risk.
The contagious bacterial infection mainly affects the nose and throat, and sometimes the skin.
What are the symptoms of diphtheria?
When the bacteria that cause diphtheria enter and attach to the lining of the respiratory system, they produce a poison (toxin) that can cause:
- Weakness
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Swollen glands in the neck

Help us prepare for the next emergency
The poison destroys healthy tissues in the respiratory system. Within two to three days, the dead tissue forms a sticky grey coating that can build up in the throat or nose, making it very hard to breathe and swallow.
The poison may also get into the bloodstream and cause damage to the heart, kidneys, and nerves.
How do you get diphtheria?
Diphtheria is caught through contact with an infected person through droplets from their respiratory tract—it is particularly spread by coughing or sneezing.
Treating diphtheria
Patients with diphtheria need to be admitted for monitoring and isolation. The sooner they receive treatment, the higher the chance of their recovery.
Patients receive antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria from the throat and an infusion of antitoxins to neutralise the circulating toxin and avoid complications.
During the recovery phase, patients need to receive a full course of immunisation – having had diphtheria does not give automatic protection against it.
The diphtheria anti-toxin is the primary means of reducing mortality and the risk of other diphtheria-caused complications, such as myocarditis (damage to the heart muscle) and neuropathies (nerve damage). Antibiotic treatment for 14 days helps reduce transmission.
It is also crucial that people who were in close contact with the patient receive antibiotics for prevention and potentially the vaccine. This will prevent them from developing the disease and halt transmission, and therefore help stop the outbreak.
Preventing diphtheria
Vaccines preventing diphtheria became available in the late 1940s in Europe and North America. But prior to the successful vaccination programme, diphtheria was very common and one of the leading causes of death in children.
Toxigenic strains of diphtheria still circulate in all regions of the world, and the disease can re-emerge if a population’s overall protection decreases, as was the case in Eastern Europe in the 1990s.
Where is diphtheria found?
Diphtheria cases have been recorded as a result of the war in Yemen and Rohingya refugees fleeing Myanmar.
“Globally, the decline of diphtheria in recent years was accompanied by a concrete loss of knowledge regarding its treatment,” says Marc Poncin, MSF’s emergency coordinator in Ibb, Yemen.
“To treat diphtheria, patients need to be isolated and receive antibiotics and anti-toxins. But the global supply of the anti-toxin, which is the single most important aspect of treatment, is very limited, and no anti-toxins were available in Yemen prior to a few weeks ago.”
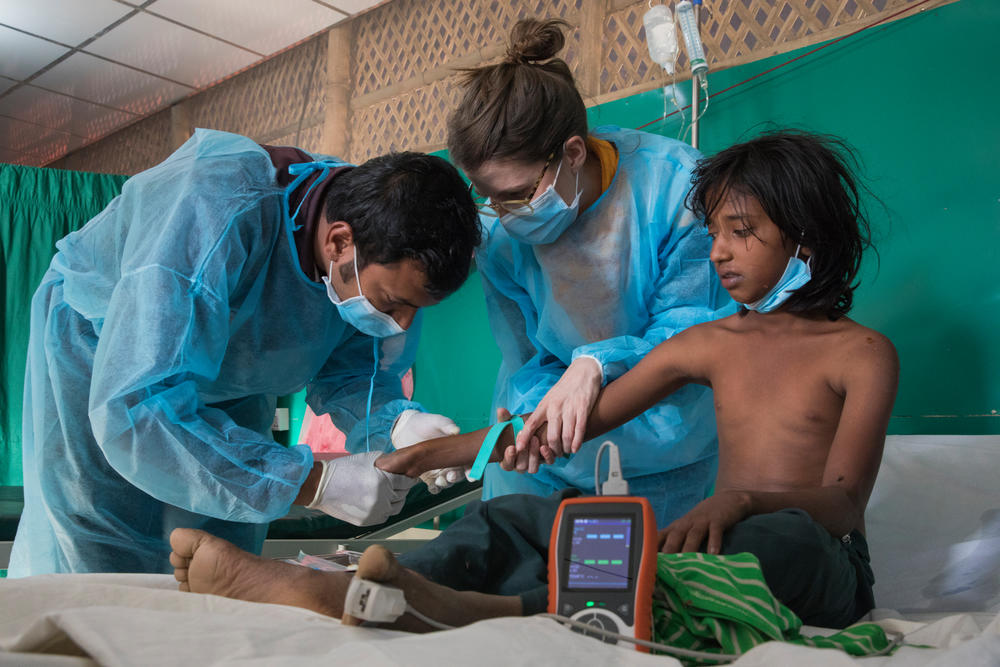
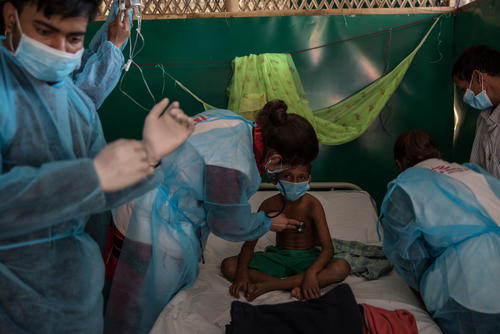
Spotlight: Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh
In 2018, MSF teams continued to see cases of diphtheria across Yemen, treating 570 patients in Abs, Ad Dhale, Ibb and Taiz. We also conducted 412,300 routine vaccinations, including DTP, which protects against diphtheria, worldwide.
In response to the Rohingya refugee crisis, we have treated more than 7,000 people for diphtheria in Bangladesh's Cox’s Bazar district as of the end of June 2019.
Diphtheria: Key facts
40%
OF DIPHTHERIA CASES CAN BE FATAL
IMMUNISATION
IS THE BEST PROTECTION
14 DAYS
ANTIBIOTIC TREATMENT NEEDED TO REDUCE TRANSMISSION
Diphtheria: News and stories