Sudan: Hope, healthcare and donkeys in Darfur
In an isolated and volatile region of Sudan, a Médecins Sans Frontières / Doctors Without Borders (MSF) team are bringing healthcare to cut-off communities in the only way possible.
Nasteh Shukri Mahamud, MSF’s medical team leader in Rokero, shares his experience from this unique life-saving project.
In early September, I began work as MSF’s medical team leader in Rokero, an area with around 200,000 people. Our project provides medical services across two areas, Rokero and Umo, in the mountainous region of Darfur state called Jebel Marra.
Darfur has suffered through over a decade of conflict. Even though much has changed following the ousting of Sudan's former president Omar al-Bashir and the installation of the new transitional government, the overall security situation remains fragile and violent clashes continue.
Rural and remote
In February, MSF started providing medical services at a state-run health centre, known as a “rural hospital”, in Rokero.
Here, we manage the inpatient department, the emergency room, the maternity and delivery wards, as well as an observation room where we keep patients under surveillance for 24 hours until they can either be safely discharged or are admitted as inpatients.We also run an inpatient therapeutic feeding centre for malnourished children suffering from complications like diarrhoea or a respiratory tract infection.
Patients with complicated injuries or health conditions are taken to a larger hospital in Al-Fasher town, the capital of North Darfur, which is six hours away by car.
"Clashes continue to erupt, and we continue to treat injuries caused by the fighting. At night we can often hear gunfire."
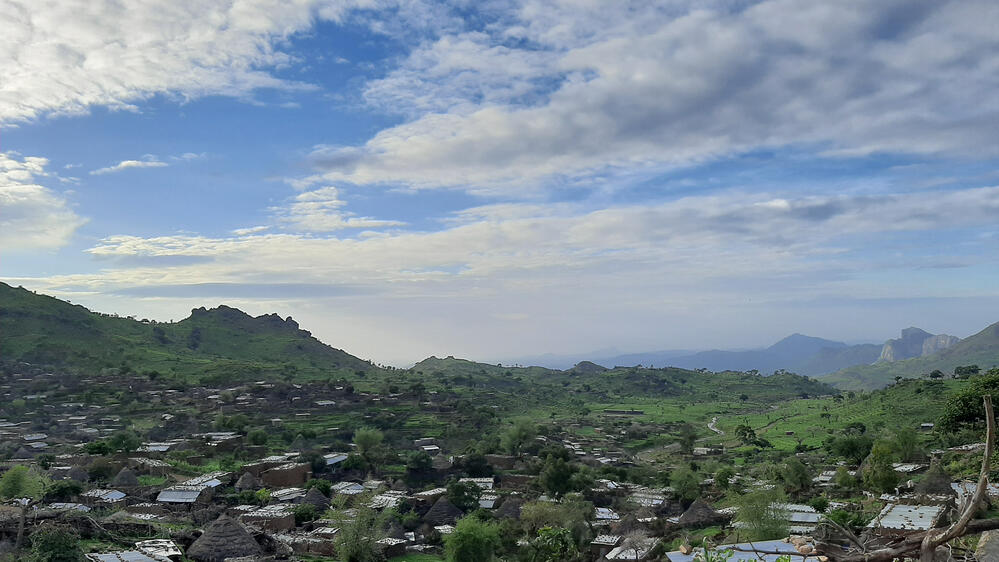
The other area, Umo, is a remote area nestled between two mountains in the Jebel Marra mountain range.
It is controlled by an armed rebel group that continues to fight government forces and other armed groups in the region for power and the control of resources. Around 50,000 people live in Umo in dozens of villages scattered over the vast rocky terrain, however, the area has been cut off from outside assistance since 2008.
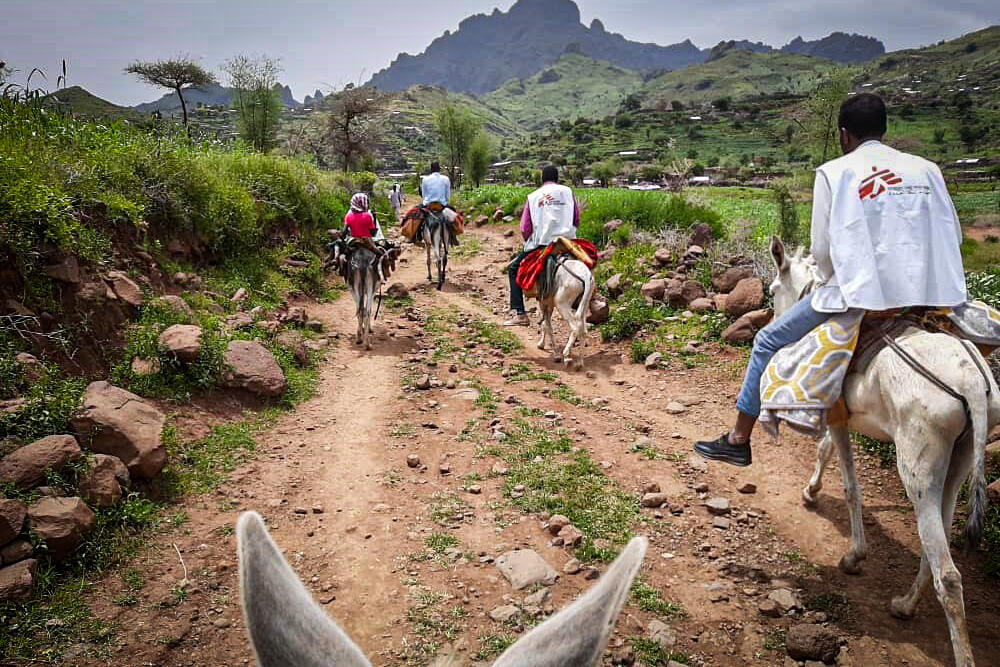
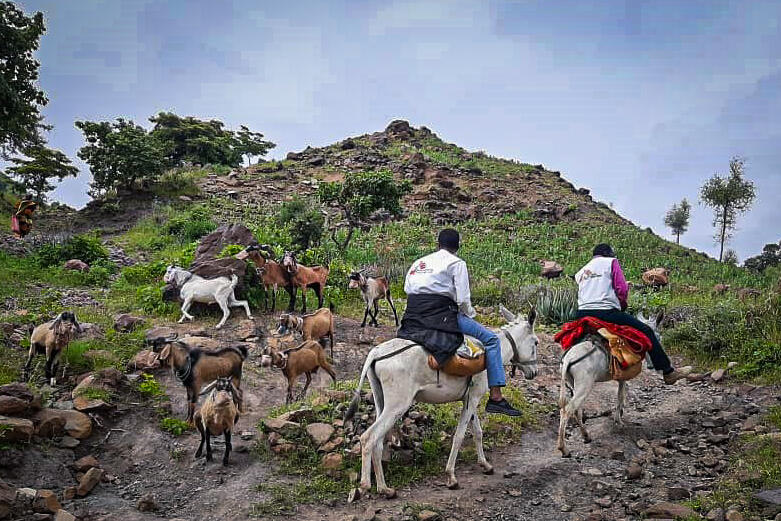
The only means of transport in and out of Umo is by donkey or camel. There are no roads, and no access for cars or busses. It is a four-hour ride from Rokero to Umo. It is a very tiring, difficult and dangerous journey along rocky, slippery ground.
Instability
The situation in both Rokero and Umo remains volatile.
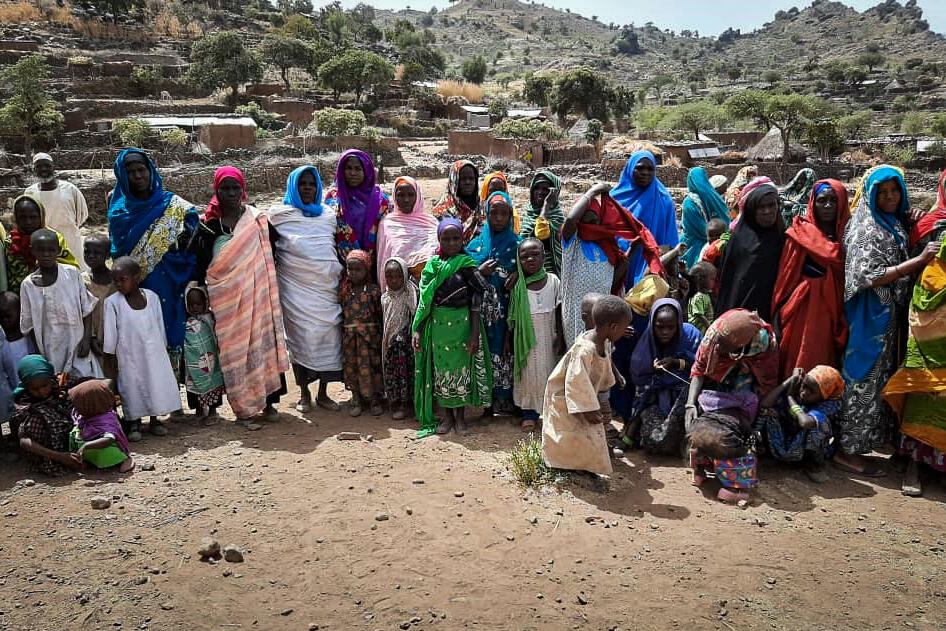
Many families that were displaced by previous conflicts found refuge around Rokero town and still live here. People continue to flee from violence from their villages to safer areas near bigger towns.
Clashes continue to erupt, and we continue to treat injuries caused by the fighting. At night we can often hear gunfire.
Many communities in Rokero and Umo depend heavily on humanitarian assistance. Approximately 60 per cent of the population have no access to basic healthcare services. Out of 20 healthcare facilities in the area only eight are functional, including the two MSF health centres.
Opening up in Umo
Our plans for 2020 were slowed down by the spread of COVID-19, but in early September we were able to open a small basic healthcare centre in Umo.
When the team arrived for the first time, the whole village, including elders, women and many children, welcomed us with excitement and anticipation.
1,061,200
OUTPATIENT CONSULTATIONS BY MSF IN SUDAN IN 2024
20,400
BIRTHS ASSISTED BY MSF IN SUDAN IN 2024
11,300
CHILDREN ADMITTED TO INPATIENT FEEDING PROGRAMMES BY MSF IN SUDAN IN 2024
Since then, we have served this community six days a week, with a team of 20 experienced and dedicated Sudanese MSF staff – some from Umo, some from other parts of Darfur. We can treat as many as 70 patients in a day.
People in Umo often suffer injuries from falls or riding accidents, and it is still an active conflict area, so gunshot wounds are also quite common. Now, at the end of the rainy season, we are treating more upper respiratory tract infections and skin diseases caused by the poor living conditions.
Eight hours on a donkey
On my first the trip to Umo, we met with community elders to better understand the lives they lead, their expectations of MSF and their health needs.
Our meeting was warm and very welcoming. The villages have been working hard to improve their living conditions. They have built some infrastructure, like stone pathways, but they have not had a functioning health centre in over a decade.
It is a difficult journey to Umo, especially now during the rainy season when tracks become muddy and untrustworthy.
"She has changed so much in just a week. She is active and enjoys eating again. Her mother could hardly believe how quick she has improved."
I was glad I had learned to ride a horse with MSF in Ethiopia in 2012, when I worked in a nutrition project that could only be reached with a one-hour ride. But, on that day in Darfur, I sat on a donkey for eight hours… back in Rokero, I had to walk around for 10 minutes just to feel my legs again.
I have enormous admiration for our drug dispenser Najmadin Aden Mahamed, who does the trip at least once a week to bring in supplies and drugs.
Complications
It is difficult to imagine what that journey would be like for a woman from Umo experiencing complications while giving birth.
In fact, the number of deaths among pregnant women and new mothers is high in Darfur. When we met with the community elders, they also told us that some women lose their babies in the first trimester of their pregnancy because they ride donkeys and work too hard.
The number of women giving birth in the MSF delivery room is still low, but we have started to do more community outreach activities, speaking with community elders and engaging with traditional birth attendants. The antenatal check-ups, however, are already attended by many pregnant women.
Most people here are farmers, growing sorghum and millet, but years of conflict have frequently disrupted farming, leaving families without their crops or with only a poor harvest.
Adding to this, an economic crisis in Sudan means that many families cannot afford the escalating prices for staple products. Most can barely afford two basic meals a day. This means women have to work especially hard, tending to both the fields and their children.
Overwhelming distance
Our team are very concerned about malnutrition among Umo’s children. During our first month in Umo, the outpatient therapeutic feeding centre treated 60 severely malnourished children.
Back in MSF’s inpatient therapeutic feeding centre in Rokero town, we usually have at least five or six children who are severely malnourished and suffering from complications like diarrhoea or respiratory tract infections.
There is a two-year-old girl currently being treated at the feeding centre. Her mother brought her in seven days ago. She had severe acute malnutrition; she was weak and much too small for her age.
However, she has changed so much in just a week. She is active and enjoys eating again. Her mother could hardly believe how quick she has improved.
She was also surprised that our medical services are free of charge.
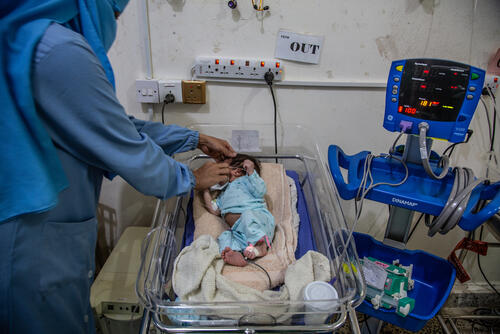
Yemen: A game-changing treatment for newborns
Nurse Alison Moebus shares this story of life-saving innovation
Distances in this isolated region can be overwhelming and life-threatening. They make it nearly impossible to access timely emergency care. People die on the way to our health centre, or reach Rokero too late for their condition to be treated.
In our first month in Umo, we lost two patients on the way to Rokero. As a medical professional this is hard to accept. We also hear of sick people that live in rebel-held areas and so are too afraid to seek healthcare in Ministry of Health facilities.
Cautiously optimistic
It is rewarding to work with such an experienced and dedicated team. We have 52 members of staff in Rokero and 20 in Umo, mostly from Darfur.
Our medical activity manager, Ali Mohamed Doud, is an emergency doctor who has worked with MSF in many different crises across Sudan.
Ali, as well as our other colleagues, know from their own experiences the hopes and worries of people in Darfur. They know too well that many communities in Jebel Marra struggle to access the basics, like primary healthcare, clean and safe water, education and protection.
Some are cautiously optimistic about a recently signed peace agreement between the Sudanese transitional government and some rebel groups. There is hope it could be a first step toward peace, reconciliation and stability in Darfur, and a chance for the many hundreds of thousand displaced people to return home.
I am proud to be a member of such a team. Directly responding to acute healthcare needs in a place where services are still very limited, and helping to save lives in a place that has long been neglected.
MSF in Sudan
Sudan was once the largest and most geographically diverse state in Africa before decades of civil war led to a split with the south.
However, tensions remain in the region and by the end of 2018, there were nearly two million internally displaced people in Sudan, along with thousands of South Sudanese refugees and many other migrants in transit to Europe.
Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders (MSF) has been working in Sudan since 1979. We continue to care for those displaced by violence and are stepping up efforts to combat kala azar (visceral leishmaniasis), a parasitic disease transmitted by sandflies that can be fatal if left untreated.